Finn O'Brien
Last updated: 12 January 2026
In this article, you will find:
Navigation guidance for accessing the information asset register.
The process of using the information asset register.
The Information Asset Register, as the name suggests, allows you to create and store information about your organisation's information assets. These can range from certain files and customer records, to entire databases. Using this area you can collate all of your assets into one area, making it both easy to manage, and for auditors to access and review.
It can be accessed by selecting the Information Asset Register button from within Compliance > ISMS, as shown below:
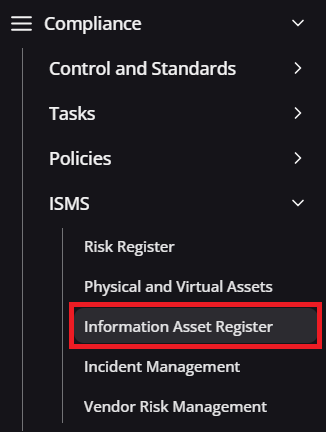
Information asset register navigation guidance
Once inside the Information Asset Register, you will see a page similar to the following:
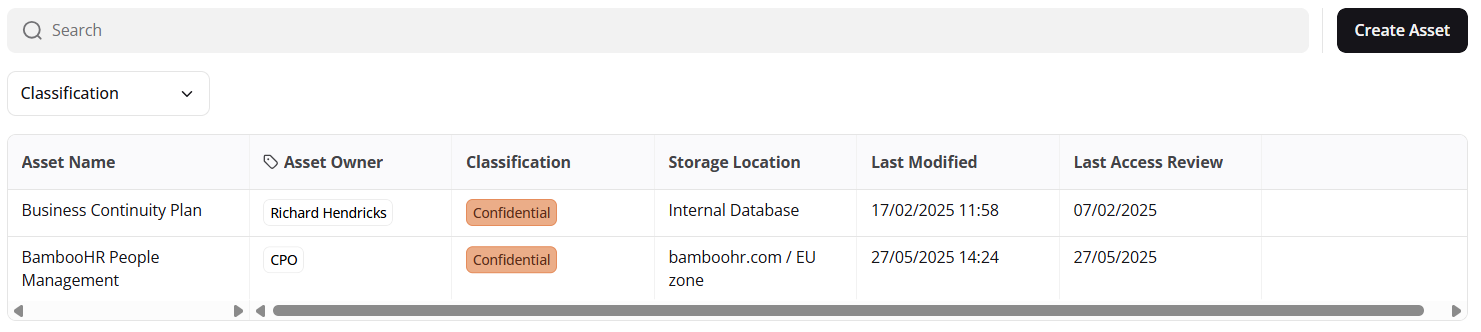
Example information asset register
As shown above, a Business Continuity Plan has been logged in the register. Assets recorded in the register are broken down into several different sections:
Asset Name: The name of the asset in question.
Asset Owner: Who is responsible for the asset, either within the platform or within the organisation.
Classification: How sensitive the asset is.
Storage Location: Where the asset is stored within the business.
Last Modified: A timestamp of when the asset was last changed or updated.
Last Access Review: A timestamp of when the asset was last reviewed. This should be on a regular basis to ensure accuracy with any new internal guidelines or processes.
You can create/store information assets by pressing the Create New asset button, located at the top right of the page. Doing this will open a side window where you can add the following information:
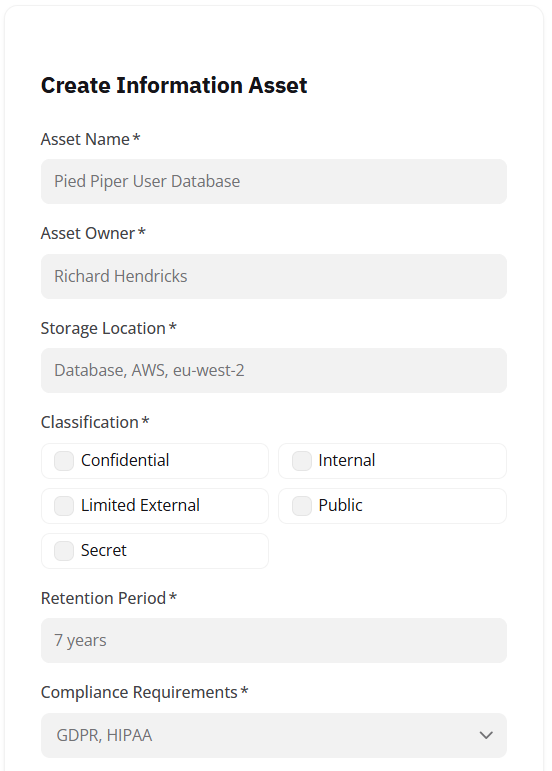
Asset creation area
Asset Name: The name of the asset.
Asset Owner: The employee in charge of the asset.
Storage Location: Where the information is stored.
Classification: Whether the information is confidential, secret, public etc.
Retention Period: How long the information is held for.
Compliance Requirements: Whether the information relates to, or is impacted by, and compliance standards.
Encryption: What methods of encryption the asset is protected by.
Last Access Review: The date of the last access review.
Access Control: Whether there are any access controls in place for this asset.